Degenerative disc disease might sound alarming, but understanding its progression can help you manage and address the condition effectively. So, what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease? This condition develops gradually, affecting the spinal discs that act as cushions between your vertebrae. These discs play a vital role in maintaining flexibility and absorbing shocks during movement. When they deteriorate, it can lead to discomfort, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Here, we’ll break it down step by step, exploring the degenerative disc disease stages and providing insights into what you can do about them. By the end, you’ll have a better grasp of its symptoms, causes, and treatment options to keep your spine in check.
What Is Disc Degeneration Disease?
Disc degeneration disease refers to the gradual wear and tear of the spinal discs, the cushions between the vertebrae in your spine. The discs absorb shock, thus allowing flexibility and movement. Over time, factors like aging, injury, or repetitive strain can cause these discs to lose their elasticity and strength, leading to discomfort and mobility issues.
One of the early signs of disc degeneration is mild stiffness or occasional pain after prolonged physical activity. As the condition progresses, symptoms of degenerative disc disease can include chronic back pain, reduced range of motion, and even tingling sensations in the limbs due to nerve compression. Lumbar disc degeneration is particularly common, as the lower back bears much of the body’s weight, making it prone to spinal disc wear and tear. Understanding these signs early can help in managing the progression of disc disease effectively.
What Causes Degenerative Disc Disease?
The main causes of degenerative disc disease often relate to lifestyle, genetics, and natural aging. Here are some primary factors that contribute to the condition:
- Aging: As we grow older, the spinal discs naturally lose hydration and elasticity. This gradual loss leads to spinal disc wear and tear, which makes them less effective at absorbing shocks. Over time, this can result in stiffness, discomfort, and reduced flexibility.
- Injury: Accidents, falls, or repetitive stress from heavy lifting or strenuous physical activities can speed up disc degeneration. These injuries often damage the outer layer of the discs, leading to further complications over time.
- Genetics: A family history of spinal issues increases the likelihood of experiencing degenerative disc disease. If your parents or close relatives have dealt with chronic back pain causes, there’s a higher chance you might too.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, poor posture, and lack of exercise all contribute significantly. Smoking reduces blood flow to the spinal discs, impairing their ability to repair themselves. Poor posture and prolonged periods of inactivity can strain the lower back, leading to degeneration of the lower back discs.
Recognizing what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease helps identify these causes early, allowing for better prevention and care.
What Are the Risk Factors for Degenerative Disc Disease?
Certain factors can make you more susceptible to degenerative disc disease. Here are some key contributors:
- Obesity: Carrying extra weight puts significant strain on the spine. Over time, this additional load accelerates spinal disc wear and tear, increasing the risk of degeneration in the lower back discs.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular movement weakens the muscles that support the spine, making the spinal structure more vulnerable. A sedentary lifestyle can also worsen the progression of disc disease over time.
- High-Impact Activities: Engaging in sports or jobs that involve heavy lifting, bending, or twisting motions puts repetitive stress on the spinal discs. This can lead to early signs of disc degeneration and exacerbate existing conditions.
- Smoking: Smoking significantly reduces blood flow to the spinal discs, limiting their ability to repair and stay hydrated. This accelerates the overall deterioration of the discs.
Addressing these risk factors is crucial in managing what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease effectively.
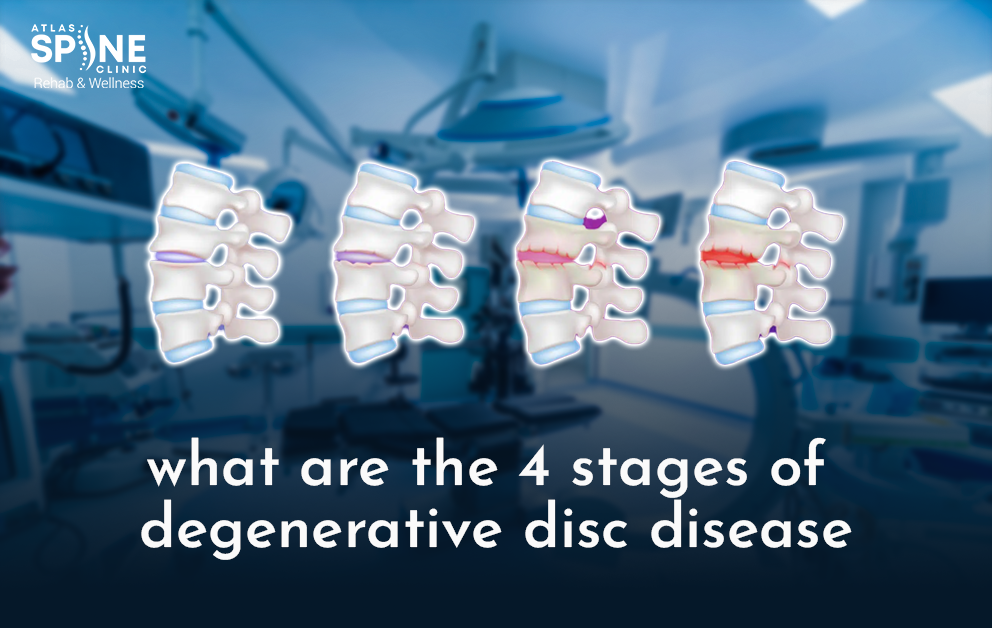
Stages of Degenerative Disc Disease
Let’s explore what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease and how they affect your spinal health:
Stage 1: Disc Degeneration (Initial Changes)
In this early stage, the spinal discs begin to lose hydration and elasticity. You might notice minor discomfort or stiffness, but it’s often manageable. Early signs of disc degeneration include occasional back pain after physical activity or prolonged sitting. Although this stage may seem mild, it sets the foundation for more significant issues if left unaddressed.
Stage 2: Prolapse (Bulging Disc)
At this point, the affected disc starts to bulge outwards, which can press on nearby nerves. Symptoms of degenerative disc disease become more noticeable, such as persistent back pain, tingling, or numbness in the legs. This is commonly referred to as a “bulging disc” stage, and the discomfort may radiate to other parts of the body. Regular activities can start to feel restrictive, making this stage more challenging.
Stage 3: Herniation (Ruptured Disc)
As the condition advances, the outer layer of the disc may rupture, allowing the inner gel-like substance to leak out. This stage is often associated with severe pain, inflammation, and limited mobility. Chronic back pain causes significant difficulty in daily tasks, and nerve compression may lead to muscle weakness or more serious complications. At this stage, medical intervention is usually necessary to manage the symptoms effectively.
Stage 4: Severe Degeneration (Advanced Changes)
The final stage involves significant disc collapse and spinal instability. Spinal disc wear and tear results in chronic pain, reduced mobility, and in some cases, disability. The spine loses much of its flexibility, and the risk of nerve damage increases significantly. Without proper care, this stage can severely impact the quality of life, making it the most challenging to manage without medical or surgical intervention.
Acknowledging what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease empowers individuals to seek early treatment and avoid severe complications.
What Is the Treatment for Degenerative Disc Disease?
Treatment options for degenerative disc disease range from conservative measures to surgical interventions. Here are some effective ways to manage the condition:
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the muscles that support the spine can alleviate pain and improve mobility. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises that reduce pressure on the affected discs and enhance overall spinal health.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or prescription medications can help manage symptoms. These treatments are particularly useful during flare-ups or periods of intense discomfort.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, improving posture, and quitting smoking can slow the progression of disc disease. Regular exercise, especially low-impact activities like swimming or walking, can support spinal health without adding strain.
- Injections: Cortisone injections may reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain. These are often recommended for individuals experiencing from these severe symptoms
- Natural Remedies: Gentle stretches, hot and cold therapy, and regular exercise can be beneficial for managing lumbar disc degeneration. These approaches promote circulation, reduce stiffness, and improve flexibility.
When considering what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease, treatment should align with the severity and progression of the condition.
When Should I Consider Surgery?
Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief. You might need to consider surgical options if:
Pain Significantly Affects Your Daily Life
If chronic back pain becomes debilitating and interferes with work, social activities, or even basic tasks, surgery might be the next step.
Nerve Compression Leads to Weakness or Loss of Bladder Control
Severe lumbar disc degeneration can compress the nerves, causing symptoms such as muscle weakness, difficulty walking, or loss of bladder or bowel control. These symptoms require urgent medical attention.
Risk of Permanent Nerve Damage
Prolonged nerve compression may lead to irreversible damage, making early surgical intervention crucial.
Common surgical procedures include spinal fusion and artificial disc replacement, both designed to relieve symptoms of degenerative disc disease and improve quality of life. Post-surgery rehabilitation and lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in ensuring long-term recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding what are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease can help you recognize symptoms early and take proactive steps to manage your spinal health. For more information and expert care, visit Atlas Spine Clinic. From minor discomfort to severe degeneration, each stage presents unique challenges, but early intervention can make a significant difference. Whether through lifestyle changes, therapy, or medical treatment, addressing the condition promptly ensures a better quality of life. If you’re experiencing persistent back pain or other related symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Stay informed and proactive—your spine will definitely thank you for it later!